Living Beings Examples on earth
A living being is all that creature that is born, grows, feeds, reproduces and dies. In this sense, a living being is an organized unit capable of capturing elements of its environment to produce and maintain its internal structures, react to changes and multiply.
Thus, a living being takes resources from outside to “build” itself, moves if something is bothering it and can create another living being similar to it.
Defining a living being is not an easy task. In fact, if we wanted to define what is a living being in another planet or galaxy, we would probably have to take into account other characteristics.
For now, on planet Earth, every living being is made of cells . Any action produced by a living being is determined by its cells and the content of them. A simple living being is an organism .
Characteristics of living beings
All living beings share key characteristics that, together, serve to define what life is. These characteristics are:
Order
Living organisms have ordered structures that coordinate with each other. All living beings are made of one or more cells. In multicellular organisms, such as humans and animals, cells are organized into tissues, tissues into organs and organs into organ systems.
It is also the case of unicellular organisms. Within the cell itself there is an order and an organization that contributes to maintaining the vital functions of the cell.
Response to stimuli
All living beings interact with their environment by responding to different stimuli, for example, plants grow in response to light. A stimulus is any physical or chemical agent that causes a reaction in an organism . In the previous example, light represents the stimulus that causes the plant to grow.
When you put your hand to the fire, you feel pain. This causes you to move your hand away as a mechanism to protect against pain and the consequences of a burn. Are you alive!
Living beings grow and develop. A child was initially an embryo, then a baby, and eventually grows into an adult.
The same goes for plants and animals. From the seed comes a seedling that can grow into a tree. A chick initially came out of an egg. All these changes are recorded in the DNA of each organism.
Homeostasis and regulation
Homeostasis refers to the ability of organisms to maintain their internal conditions at stable and constant levels . For this, living organisms have regulatory mechanisms. Humans maintain their temperature at 37 ° C, whether they are in cold or warm environments.
Metabolism
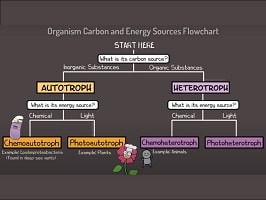
Life is a sum of interconnected chemical reactions , which require energy and nutrients to be carried out. Plants use the sun’s energy to obtain their nutrients; animals require feeding on other living beings to maintain their metabolism.
All organisms need to feed themselves to survive. Those beings that produce their own food are known as autotrophs, while those that feed on other living beings are heterotrophs.
Reproduction
Humans have babies, dogs have puppies and plants have seeds. This is what we call reproduction. When living beings reproduce they pass on their genetic information to their children. Even unicellular beings reproduce!
Living beings multiply through different mechanisms of reproduction, either by cell division or by specialized structures.
In plants, the flower is the structure of reproduction. In animals, many species differ in male and female, with specific reproductive organs.
Evolution
Evolution is the ability of organisms to survive over time through adaptation to environmental conditions and the transmission of these characteristics to their offspring .
The characteristics of the organisms that help them adjust to their environment are called adaptations. For example, the chameleon can change the tone of its skin to go unnoticed by its prey.
Classification of living things
Living beings can be classified into three large groups or domains. The three domains of life are:
- Bacteria : prokaryotic unicellular organisms, that is, their DNA is not wrapped in a nucleus.
- Archaea : they are also prokaryotic unicellular organisms, which are differentiated from bacteria by their cell wall.
- Eukarya : in this domain are plants, animals, fungi and algae. They are characterized mainly by the fact that their DNA is inside a nuclear membrane, that is, they are eukaryotes.
The domains in turn are divided into realms. The best-known kingdoms are the kingdom Animalia (animal), the kingdom Plantae (plant), the kingdom Fungi(fungi) and the kingdom Eubacteria (bacteria).
The classification of the alive beings continues by the Phylum , the classes, the order, the family, until arriving at the sort and the species. The genus and the species of a living being are like his surname and his name, what we know as the scientific name .
Composition of living beings
Of all the elements of the periodic table, living beings are composed of only a few elements. The most abundant elements are hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and carbon. Other fundamental elements, but which are present in smaller quantities, are: calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, iron, sodium and chlorine.
Are viruses living beings?
Viruses are interesting structures that have genetic material and proteins, but they are not a cell. These viruses have the ability to enter a cell, and there they take advantage of it to multiply. Without the help of the cell, which they invade, the viruses can not multiply.
We know of viruses that evolve, but we do not know how they do it. Viruses do not have metabolism, they do not need food to survive, nor do they need regulation mechanisms. For all this, viruses are not considered living beings.