What Are The Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells?
The cell is the basic unit of life. All the activities of life are done by cells. The organisms are classified based on the number of cells present in them.
Unicellular organisms are single cells. On the other hand, Multicellular organisms have a large number of cells. Plants play the role of producers in an ecosystem, whereas animals play the role of consumers. As a result, both their cell structure and everyday tasks and roles are different.
Animals and plants have several cell organelles, which are usually categorized according to their functions. The distinction between plant and animal cells is caused by the different cellular makeup of each.
Both cells are classified as eukaryotes since they have a defined nucleus where the genetic material is stored. In addition, they distinguish a plasma membrane, membranous organelles such as mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, and cytoskeleton.
Differences Between Plant And Animal Animal Cells Diagram
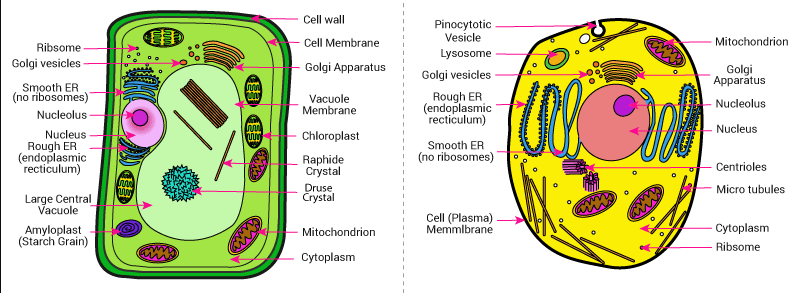
The unique difference between plant and animal cells is that Animal cells are those found in animals and plant cells are those found in plants and algae. The other difference between animal and plant cells is the presence of a cell wall and chloroplasts in the plant cell.
The following table summarizes the differences between these cells:

What is a Plant Cell?
The plant cell is a eukaryotic cell that is characterized by the presence of a cell wall that gives it support and protection while allowing cell communication. This wall can be found in other types of eukaryotic cells.
Like the animal cell, it has a differentiated nucleus, membrane, and cytoplasm.
However, the plant cell contains unique parts that are responsible for the process of photosynthesis. Something fundamental, because it allows plants to release the oxygen that living beings need to exist.
Plant cell characteristics
Nutrition
The nutrition of plant cells is autotrophic, so they are capable of synthesizing all the nutrients they need from inorganic material. That is, they are independent of other living beings to obtain their nutrients.
Energy
The chloroplasts present in plant cells are responsible for carrying out the process of photosynthesis, where sunlight is used as an energy source. This is possible with the help of chlorophyll, a substance present inside chloroplasts that absorbs sunlight.
These chloroplasts lie next to the membrane and measure approximately 5 micrometers.
Cellular wall
The most prominent feature of plant cells is the cell wall that surrounds the plasma membrane. This wall is composed mainly of cellulose and can measure between 0.1 and 10 microns.
The cell wall provides protection, stability, and rigidity to the plant cell.
vacuoles
Plant cells have a single large vacuole that can cover up to 90% of the cell.
cytokinesis
In plant cells, after the division of the nucleus occurs, an accumulation of vesicles of the Golgi apparatus occurs. These vesicles fuse and give rise to a new cell wall between the two cells.
Plasmodesmata and glyoxysomes
Plasmodesmata are found in plant cells, which are pores in the cell wall that allow molecules to pass between plant cells.
Glyoxysomes are organelles found only in plant cells. In these structures, lipids are stored and degraded, mainly in seeds in the germination process.
What is an Animal cell?
The animal cell is a eukaryotic cell characterized by the presence of a nucleus, plasma membrane, and cytoplasm. It differs from the plant cell by the absence of a cell wall and chloroplasts. In addition, smaller and more abundant vacuoles can be found compared to those of a plant cell.
Animal cells can take various forms. They are also capable of capturing and digesting other structures.
Some of the most prominent animal cells are the neurons of the nervous system, the leukocytes of the immune system, and the eggs and sperm of the reproductive system.
Animal Cell Characteristics
Nutrition
The nutrition of animal cells is heterotrophic, which means that they need to obtain nutrients and energy from the organic material of other living things.
Energy
The mitochondria are responsible for generating energy in the animal cell, through the process of cellular respiration. In this process, ATP is produced from glucose.
Mitochondria are equivalent to the chloroplasts present in plant cells since both are responsible for producing energy.
vacuoles
The vacuoles resemble sacs of water. Animal cells are usually very numerous and small. Its function is to store water, ions, and intracellular waste.
cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm during cell division (mitosis or meiosis). In animal cells it is produced through a ring of actin filaments, which squeeze the plasma membrane in half, separating two new cells.
lysosomes and centrosomes
Animal cells have lysosomes, membranous organelles that are responsible for intracellular digestion. They also possess centrosomes, which are cylindrical structures involved in animal cell division, which are not found in plant cells.



