What is the central nervous system?
We explain what the central nervous system is, what neurons are and what their functions are. How is its structure and diseases.
-
What is the central nervous system?
The central nervous system (CNS) is a structure that is formed by the brain, (which is the part of the central nervous system located in the skull) and by the spinal cord (located inside and along the entire spine).
The central nervous system is responsible for the organization of the devices ( respiratory , digestive , etc). This system has the function of coordinating, integrating and controlling the organism . It is also responsible for the reception of the stimuli that can arrive both from outside and from the organs of the same organism. Subsequently, the central nervous system is responsible for processing this information and preparing responses respectively.
The SNC is organized by hierarchies. Each hierarchy controls those below it and this, in turn, is controlled by the superior hierarchy.
The information received by the central nervous system is processed by cells that are called neurons.
-
Neurons
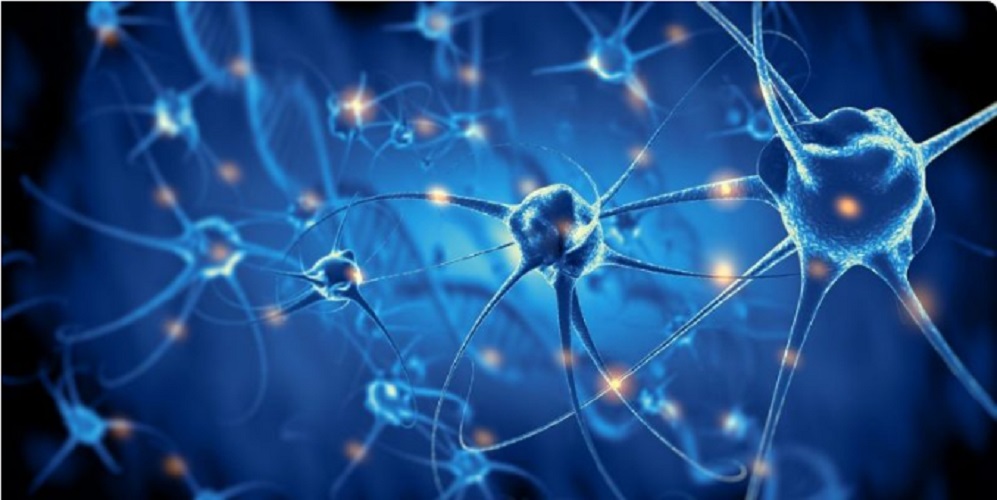
The neurons have a shape that differ from traditional cells. Neurons are made up of a soma or body . This soma has a rounded shape and is covered with hairs that are called dendrites.
Dendrites are nerve centers that receive information from other neurons. Through the excitability of the neurons it is possible that the information is transferred from neuron to another neuron.
From the soma comes an axon that is a thin and very long connection that allows information to travel through it and connect with other neurons. Thus the information leaves the axon and reaches the dendrites of another neuron, which receives this information, processes it in its soma and sends the information received to the dendrites of another neuron.
In this way, neurons connect with each other and allow information to travel from one place in the body to another.
The distinguishing feature of neurons is that information travels extremely quickly, through nerve impulses thanks to the myelin that exists and covers the axon.
-
Central nervous system structure
As we have said above, the central nervous system is subdivided into two parts: one that is inside the skull and the other inside the spine. The first is called the brain and the second, spinal cord.
Brain structure. In humans and vertebrates, the brain is divided into:
- Previous brain . It is also called pros encephalon .
- Middle brain . It is also called midbrain and is the upper structure of the brain stem.
- Posterior brain . It is also known as a rhombencephalon and is located in the immediately superior part of the spinal cord. In turn, this can be subdivided into three parts:
- Bulb
- Annular protuberance
- C erebelo
Structure of the spinal cord. As we have said before, the spinal cord is inside the spine. This area is known as a spinal canal or spinal canal.
The spinal cord has the function of bringing nerve impulses to the spinal or spinal nerves, that is, its function is to communicate certain information to the peripheral nervous system (SNP).
-
Central nervous system functions
The functions that the CNS has are classified into conscious and unconscious functions.
Conscious functions . These functions are carried out in the cerebral cortex. Some of these functions are: ideas, thoughts , memories, emotions, body movement , among others.
Unconscious functions. The f unconscious unctions are carried out in the hypothalamus. Some of these are sleep, wakefulness, the functioning of organs such as the heart, functions such as eating, drinking, etc.
Brain functions . The highest level of hierarchy in the central nervous system is that found in the cerebral cortex. In the cortex, superior functions such as conscious perception, memory , reasoning are organized . Below this, are the cerebellum and basal ganglia, these are responsible for controlling the movement consciously. Below this is the brain stem whose function is to maintain balance, control the pressure in the body, perform automatic movements such as breathing or heartbeat, chew, among others. Below these functions is the most basic level that is that of the spinal cord .
Functions of the spinal cord . Strictly the spinal cord has two functions; afferent function and efferent function:
- Afferent function : its function is to transmit the sensations of the trunk, neck and four limbs to the brain.
- Efferent function : these are the orders that start from the brain towards the different organs indicating that they perform a certain action.
-
Central nervous system diseases
- Dementia
- Epilepsy
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- Multiple sclerosis
- Mononeuropathy
- Monoplegia, hemiplegia and tetraplegia
- Neuralgia
- Diabetic neuropathies
- Polyneuropathy
- Cloistered Syndrome
- Guillain Barre syndrome
- Trauma
- Tumors