What is an individual in biology?
We explain to you what an individual in biology is, some examples and their relationship with populations, communities and ecosystems.
-
What is an individual in biology?
The individual is an organism ( unicellular or multicellular ) capable of existing by itself in a given environment. The word individual comes from undivided meaning “that cannot be divided” and refers to the being that is capable of performing all its vital functions and that is independent of those of the same species.
The individual is examined by Biology , a science that covers a wide field of study and analyzes the components that determine a being, its molecular structure, development and evolution and interrelation with other beings.
-
Examples of individual, population and community
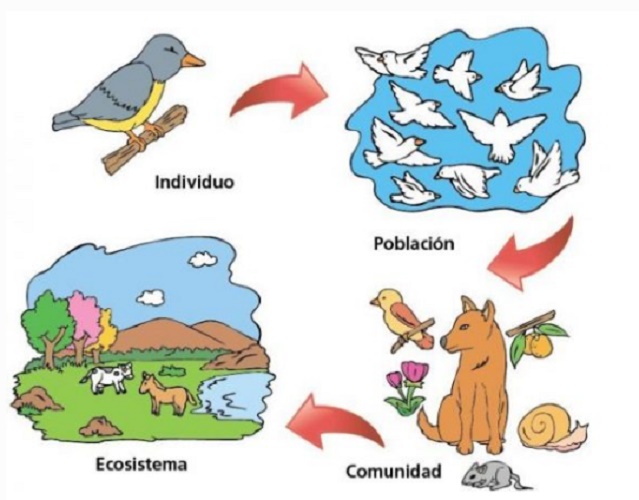
The individual presents characteristics that differentiate him from other beings. Some examples of the individual: a tiger, a hyena, a hummingbird, a dolphin, a walnut and an ombú .
Individuals are grouped with beings of the same species in a given space, what is called population . For example, a population of seals, one of humans, one of dogs, one of condors, one of walnut trees, one of ferns, etc.
The set of populations is called community , in which different groups of animals and vegetables coexist in the same territory. For example, in the same community a population of palm trees, one of parrots and one of pigeons can live together, among hundreds of other populations.
An ecosystem is the group of communities that interrelate in a geographic area with the elements considered “lifeless”, such as rocks, water , air , etc. Examples of ecosystems are a forest, a river, a mountain range, the sea, etc.
-
Community in biology

A community is made up of numerous different populations that need to be interrelated by biological issues. In the case of the human being , in addition, he needs to relate for socio-economic and psychological reasons for what is organized in increasingly industrialized cities .
Human beings tend to isolate themselves from other animal and plant populations, and increase the number of individuals in their own population. This way of life impacts the life of different animal and plant species, and generates alterations in the relationship between ecosystems around the world.





