What is the Komodo national park?
We explain what the Komodo National Park is and where it is located. In addition, its flora, fauna and other characteristics.
-
What is the Komodo national park?
The Komodo National Park, located in Indonesia, was founded in 1980 with the aim of protecting and conserving the only species of giant lizards . These reptiles are called “Komodo dragons” for their aggressive behavior and appearance (they can measure up to three meters in length and reach a weight of 70 kg.).
In 1991 the park was declared by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site and Biosphere Reserve . In addition, in 2011 it was declared as one of the seven natural wonders of the world .
Little is known about the early history of the Komodo islanders. The majority of the inhabitants of the park and the surrounding area are fishermen from small nearby islands or even descendants of nomads. There are no people of pure blood who can transmit part of their ancient culture or language.
-
Komodo National Park Location
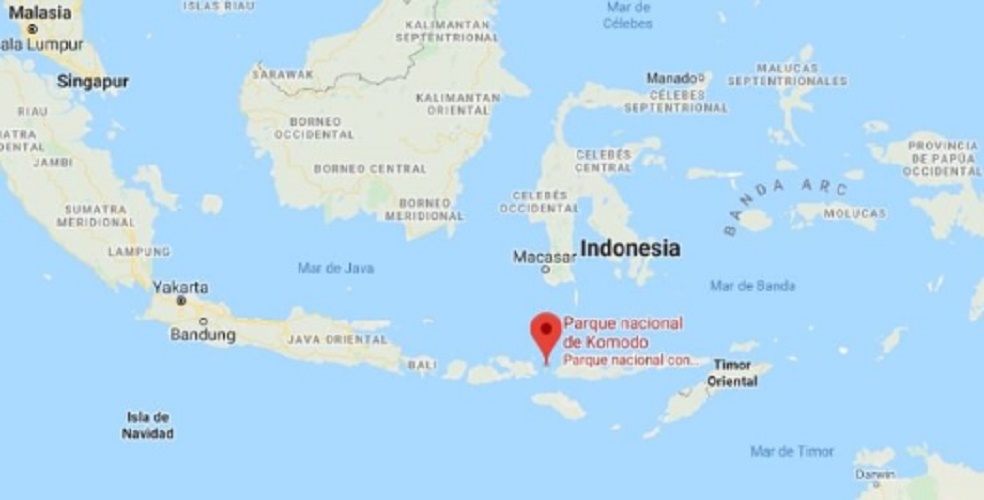
Komodo National Park is located in Southeast Asia, in a volcanic area of Indonesia . The archipelago is made up of Komodo, Rinca and Padar, three important islands that stand out for their size and that are part of the so-called “Sonda Islands”, composed of numerous smaller islands.
-
Flora and fauna of Komodo National Park

Due to the warm and dry climate, the Komodo National Park presents a typical savanna vegetation , between hills and small forests that appear only in areas that are above five hundred meters high and an intense green vegetation that contrasts with the White sand beaches and blue waters.
The great sea current is rich in nutrients and volcanic elements, which has made it possible for thousands of different species to thrive. There lives a huge variety of tropical fish, three hundred species of corals and a hundred varieties of sponges . You can even see whale sharks, dolphins, manta rays, seahorses and octopuses.
The terrestrial fauna presents a smaller diversity in comparison with the marine fauna. Many of the mammals are of Asian origin , such as Timor deer, wild boar, water buffalo, macaques and crabs. Instead, the reptiles and birds are Australian – born , as the Asian bullfrog, scrub birds orange legs, the cockatoo and the friar bird.
The most famous of reptiles is the Komodo dragon , the largest lizard variety in the world. The estimated population of these giant reptiles is six thousand inhabitants. In addition, twelve species of terrestrial snakes inhabit the area, such as the Java spit cobra, Russell’s viper, the white-lipped viper and the Timor python.
-
World Heritage

The archipelago formed by the Sonda Islands is recognized and protected worldwide. In 1938 the island of Padar and part of Rinca were established as nature reserves and in 1965 it was also established to the island of Komodo. Only in 1977 the island of Komodo was recognized as a biosphere reserve under the UNESCO Biosphere and Man Program.
Time later, in 1980, the three islands were declared “national park” , a title that was later extended to include the surrounding marine area. In 1991 the national park was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO.
Despite this, there are currently illegal fishermen who continue to exploit part of this world heritage. Thanks to the work of protectionists and entities that work to care for these territories, in the most recent years sixty illegal fishers have been arrested.
-
Komodo National Park Features

The Komodo National Park has almost four thousand people living in four settlements: Komodo, Rinca, Kerora and Papagaran. In 1928 there were only thirty inhabitants but the population grew rapidly from 1999 and currently, in the areas bordering the park, about seventeen thousand people live.
It is a very attractive place for tourists from all over the world because of the diving practices that allow you to enjoy a stunning marine biodiversity . In 2009 the park was visited thirty-six thousand tourists and in 2010 for forty-five thousand. The tourist activity is a very important strategy for the park to finance itself and continue its work.