What was the Olmec culture?
We explain what the Olmec culture was, its economy, religion, clothing and other characteristics. In addition, its main contributions.
-
What was the Olmec culture?
The Olmec culture (also simply called the Olmecs) was a pre-Columbian culture that inhabited Mesoamerica from the Formative Period (about 2000 years before Christ) until the Classic Period (400 years before Christ). It is estimated that she was the “mother” of all other Mesoamerican cultures .
The term “Olmec” ( Olmecatl ) means in Aztec language “inhabitant of the rubber region” and is the only word we have to call this civilization. In fact, we don’t know what the Olmecs called themselves.
It is possible that this name was given by the Mexican Empire to the inhabitants of the region of the current Mexican states of Veracruz and Tabasco for centuries, without distinguishing their cultural or linguistic origin.
This term was also used by 20th-century archaeologists to refer to the Olmec-Xicalanca Nahuatl culture, with which we should not confuse the Olmecs, although it is likely that there was an ancestral affiliation between the two.
Olmecs are traditionally considered to be the inaugurators of a Mesoamerican artistic and architectural style of which there are still abundant ruins, from Jalisco to Costa Rica. His motives were later adopted by the later cultures of the region. This would mean that the Olmec culture remained alive even after its decline.
Other cultures:
| Teotihuacan culture | Mayan culture |
| Aztec culture | Greek culture |
-
Geographical location of the Olmecs
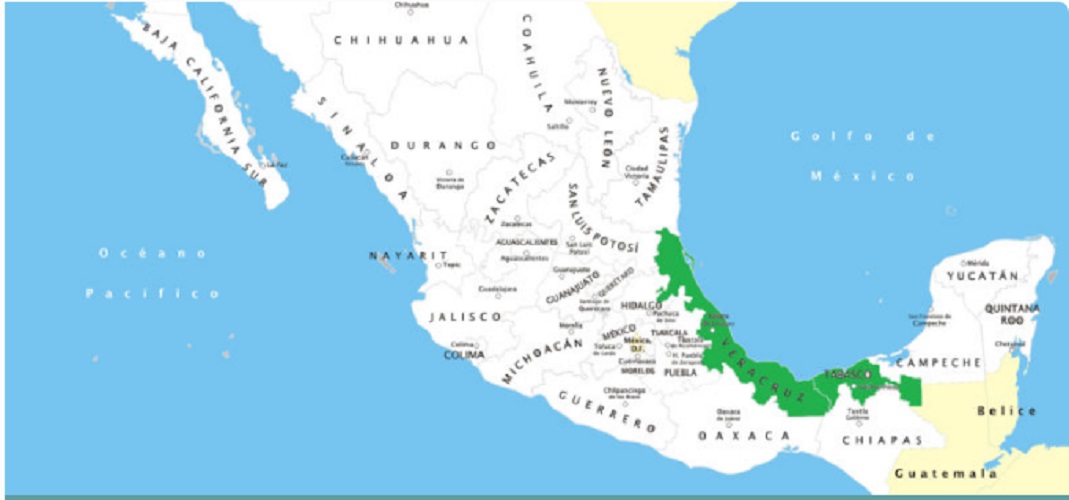
The Olmecs emerged in the southeastern region of present-day Mexico , especially in the states of Veracruz and Tabasco. Subsequently, its influence spread throughout the Mesoamerican region , in the territories of present-day Guatemala, Belize, El Salvador, Nicaragua and Honduras.
There is evidence of its origin in both Chiapas and the Central Valleys of Oaxaca, and in the Isthmus of Tehuantepec. But its main ceremonial centers were: San Lorenzo (1150 BC), La Venta (1750 BC) and Tres Zapotes (900 BC).
-
Olmec Economy
The economy of the Olmecs is likely to have been mainly agricultural , but with an important margin for trade with neighboring towns, through vast and elaborate exchange networks.
In this way their culture was adopted and distributed throughout the continent, being valued by other cultures. Rubber, abundant in the region, may have served as a good of exchange.
-
Religion and deities of the Olmec culture
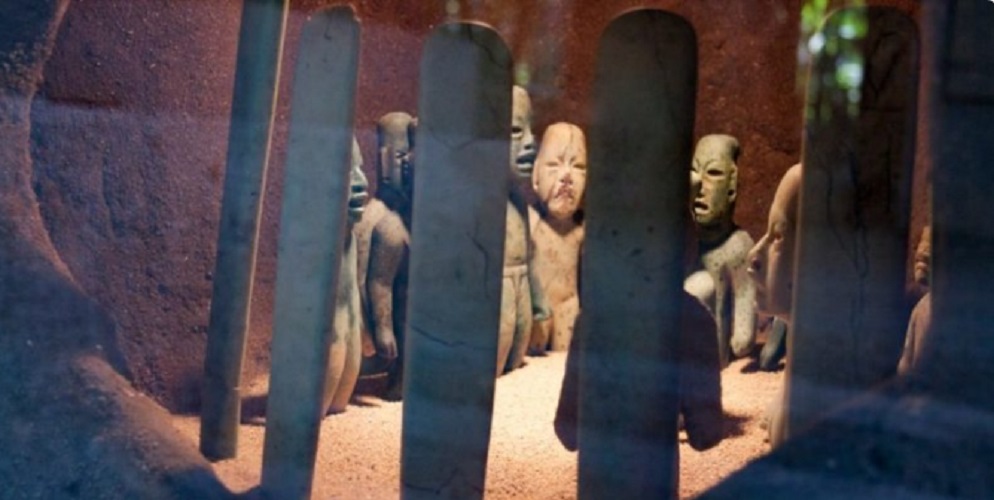

Everything indicates that the Olmec culture was deeply religious. It was theocratic, polytheistic, with fundamentally agricultural deities , representing the stars , volcanoes and other aspects of the cosmos.
They had sacred animals , such as the jaguar, which they worshiped abundantly. They also worshiped toads, alligators and a vast mythology of beings with heads of one and body of another.
It is estimated that it was a dynastic religion, that is, that linked its rulers directly with the gods , as if they were their heirs. But it was a complex religion that has not yet been fully deciphered.
Not much is known about the way the Olmecs organize themselves, but judging by the complexity of their representations, it is likely that they had a complex society, with different levels, in which warriors and soldiers played a prominent role .
-
Olmec dress
Judging by the art exhibits and preserved Olmec statuettes, this culture probably wore light clothes of cultured cotton . They also used various methods of personal ornamentation depending on the activity performed and the place within the social order and their hierarchies.
Nasal septa, feathers, nose rings and pectoral earrings were probably common in men, especially warriors. Women used to wear huipil and quechquemitl, with skirts underneath.
-
Contributions of the Olmecs
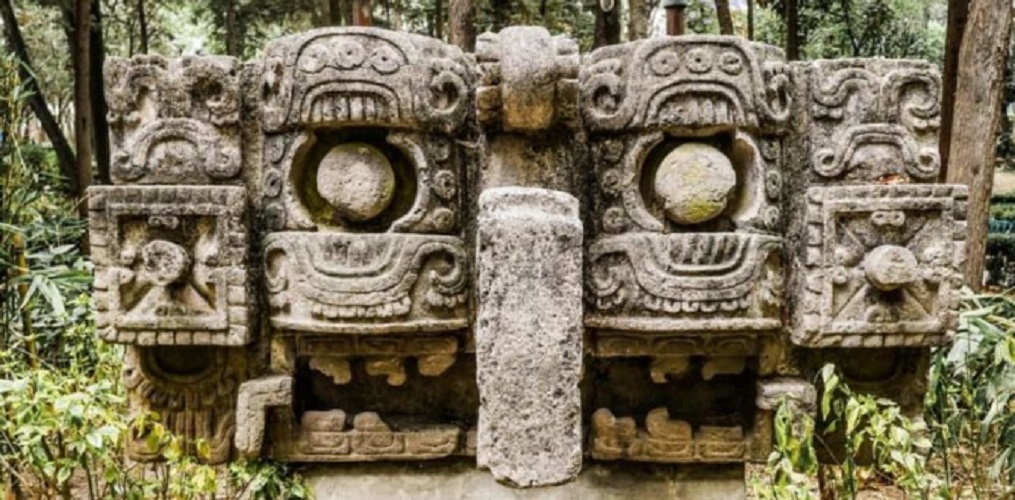

The Olmecs contributed significantly to the Mesoamerican culture and, indirectly, to human civilization, through the development of a particular artistic, architectural and philosophical style, in addition to:
- The discovery of rubber or natural latex, from rubber trees.
- Its imposing buried sculptures , which are shaped like a giant head (3 meters) and were later replicated by other local cultures.
- The construction of pyramids and ceremonial centers whose ruins inspired other later cultures.
- They were the first connoisseurs of cocoa , who knew how to turn into primitive forms of chocolate.
- They played an unknown sport , in which they used rubber balls on specially designed courts.





