What is the Mediterranean forest?
We explain what the Mediterranean forest is, its flora, fauna, relief, climate and other characteristics. Also, where is it located?
-
What is the Mediterranean forest?
It is called Mediterranean forest, durisilva or Mediterranean scrubland a forest and scrub biome frequent in regions that have a Mediterranean climate , that is, a climate similar to that of the vicinity of the European sea of the same name.
These types of forests date back to very ancient times, and have survived the formation events of the Mediterranean region (from the Tethys Sea in the Mesozoic period). On the other hand, they also resisted the intervention of the human being , who has played an important role in shaping his biocenosis.
However, the Mediterranean forest is highly sensitive to desertification , if the vegetation layer is destroyed, since it is a type of arid biome, xerophilous vegetation (adapted to the dry environment) and low biodiversity .
Currently, there are numerous initiatives to protect these forests, also threatened by climate change , whose results however do not seem very encouraging: a growth of just 2% between 2010 and 2015, according to UN figures .
-
Mediterranean forest location

The Mediterranean forests are distributed, in the world, in five climatic regions located in the western facade of different continents . These regions are:
- The endorheic basin around the Mediterranean Sea, between southern Europe, northern Africa and western Middle East.
- The chaparral californiano , located in the state of California of the United States.
- The Chilean scrubland , on the western coast of South America and in central Chile.
- The South African fynbos , located in the Cape region.
- The mallee to the southwest and south of Australia.
-
Mediterranean forest characteristics
It is a xerophilous forest, with woody, aromatic and thorny undergrowth . It contains a modest number of plant species and a tendency towards very marked desertification, either as a result of the destruction of the vegetation layer or by the erosive action of the rains on the soil .
The plant species are adapted to the fire , recurring in the drought of the summers . Therefore, they have very thick and resistant crusts with which to shelter themselves, as well as leaves covered with wax to prevent the loss of water during the warm months.
-
Mediterranean forest fauna
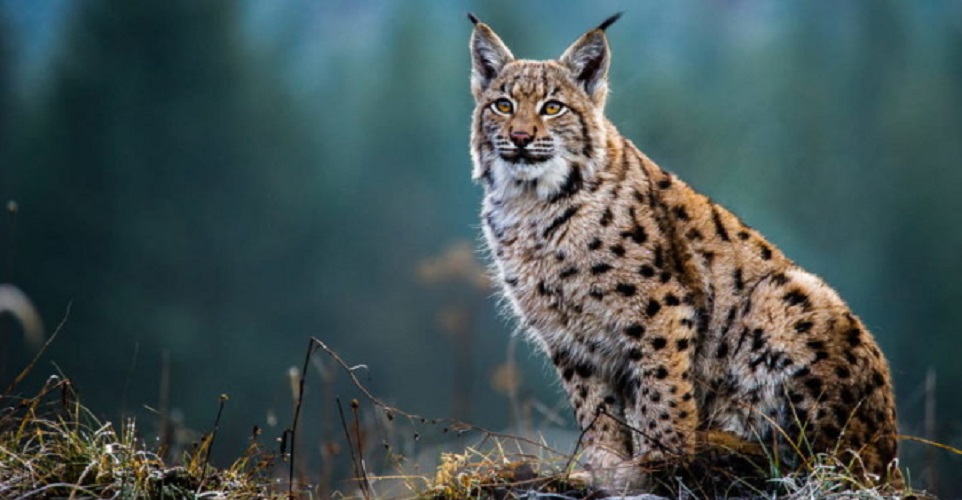

In the Mediterranean forest there is an animal diversity adapted to the climatic conditions and the vegetables available as food . As in other forests, insects are the most numerous and successful animal group, holding a food chain that includes raptors, small rodents, squirrels, hares and small reptiles .
There are also larger predators such as the lynx (especially the Iberian lynx), foxes, eagles and wolves. There are also herbivorous animals such as the mountain goat. Amphibians abound and many species of birds such as jay, piquituerto, herrerillo or chotacabras.
-
Mediterranean forest flora
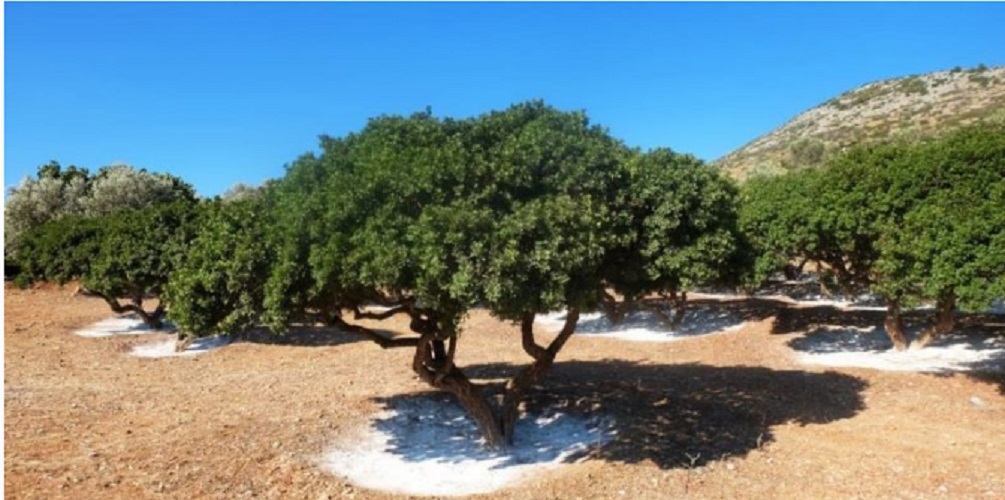

In these forests , perennifolias predominate , such as holm oak, amid a xerophilous and sclerophilic vegetation , adapted to summer aridity. There are also plenty of lentisco, aladierno, many vines such as sarsaparilla, and also jaras, rosemary and thyme.
There are species that produce flowers , such as the carrasco pine and the pine tree, the sabina or the madroño, and in the wetter regions there is abundance of the quejigo and the cork oak. When you make the transition to other regions, you usually form mixed forests with other lush scrub species, or gallery forests.
-
Mediterranean forest relief
The Mediterranean forest predominates in flat reliefs , plains, with the occasional mountain range and especially the valleys. The mountains around them are usually young, with relevant plateaus and highly populated.
-
Mediterranean forest climate
The Mediterranean climate is characterized by mild winters, warm autumns, rainy springs and dry summers , in which forest fires abound, to which the vegetation is adapted (pyrophilic vegetation).
On average, the temperature is maintained above 20 ° C , presenting seasonal variations. Precipitation is not very abundant during the year, although they can exceed 1000mm in certain regions.
This type of climate differs from both the coastal Mediterranean climate (close to the water, more stable and humid), and the continental Mediterranean climate (drier and with greater thermal variations).