What is a diagram?
We explain what a diagram is and what types of diagrams exist. Also, what is the purpose of the diagrams and why are they so useful?
-
What is a diagram?
A diagram is a graph that can be simple or complex, with few or many elements, but that serves to simplify communication and information about a particular process or system.
There are various types of diagrams that are applied according to the communicational need or the object of study : there are flowcharts , conceptual , floral, synoptic and dozens more.
Explanatory diagrams are frequently used in the field of education , communication and science itself . A diagram usually consists of small boxes, balloons and arrows that connect the parts to create a whole.
Generally it is a complete summary , which should be helped by a text or a speaker, that completes the purpose of the diagram, detailing with words what the drawing itself does not say .
-
Types of diagrams
- Flowchart : It is usually the most recognized and the most used in the work and computer areas. They detail step by step the network of functions and components in a system. It is characterized by having an oval as a starting and closing point, a rectangle to detail an action, a rhombus to graph the execution of a decision, the circle as a connecting component and the triangles to explain thenecessary files or documents.
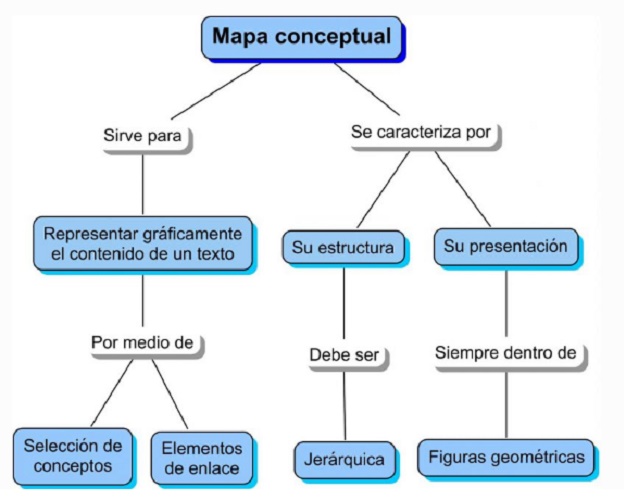
- Conceptual diagram : The concept map is very distinguished among students who study advanced subjects, since it is used to simplify the study. It can be a simple or complex graphic, according to the amount of concepts and ideas that you want to add and relate. It is more open to creativity , that is, each one can create a conceptual map at ease, but it must fulfill the function of awakening in us an acquired knowledge: with a word enclosed in a circle, the exact importance and significance must be remembered of the concept, and how it relates to others.
- Synoptic diagram : It has a greater complexity, since from a premise a true network of concepts and elements that can relate to each other can be extended widely. The condensation of knowledge as a cognitive strategy in this diagram usually presents the characteristic of braces and brackets that close or open ideas and notions.
- Floreal diagram: The floreal diagram differs from all the previous ones, since it does not include ideas but simply graphs the floral species. Through the use of diagrams you can obtain detailed information about the components that make the flower, from the largest and most colorful parts, to the minimum and microscopic characteristics, for a complete study of these objects.
- Phase diagrams : Phase diagrams use another conventional method of science that are vectors and axes. These are two arrows, one horizontal and one vertical, that are born from their perpendicular point to extend infinitely, thus creating a field of relationship between these two factors. Using lines, points and other geometric elements, you can study, analyze and solve the different states of matter in physics and chemistry .





