What is the workforce?
We explain what is the workforce and its different types: direct or indirect, qualified or unskilled, management and commercial.
-
What is the workforce?
In economic terms, labor is understood as both the physical and mental effort carried out by a worker to manufacture, repair, or maintain a good, as well as the economic remuneration that such work implies, that is, the price of services of work.
All kinds of productive initiative or services require a workforce. Precisely this capacity for work is what the working class has to exchange in the economic circuit, usually in exchange for a salary .
The total number of workers available in a country, that is, the majority of its economically active population (PEA), can be considered as its workforce. Depending on the labor, social and tax requirements of the legal system of that country, it can be more expensive or cheaper for your possible employers.
Labor in its current sense was born alongside the Industrial Revolution , when peasant workers migrated to the cities to become industrial workers.
Today it is a much more diverse population , among which are professionals and self-employed workers, as well as other sectors whose importance in the economic circuit is constantly threatened by the pressures of increasing automation and technologization of the productive process.
-
Direct and indirect labor
A first distinction within what is the workforce, requires differences:
- Direct labor : It is the one that is involved in the productive circuit. Their indispensable tasks can easily be associated with the good or service obtained. Workers in a compote factory, for example, are direct labor, attached to the company’s payroll.
- Indirect labor : It is the group of workers who do not intervene immediately in productive work, but who accompany, optimize and control it from an administrative, commercial, etc. perspective. In the case of the compote factory, the area coordinators, the marketing managers , the accountants and the people in charge of the personnel selection are indirect labor.
-
Skilled and unskilled labor

The skilled workers have received some level of education or training without which they could not carry out certain tasks (or effectively).
On the contrary, unskilled labor are those workers who have not received any type of instruction and have only their labor power to offer.
Obviously, skilled workers are always more desirable and usually cost much more than unskilled workers, since they have specialized knowledge and / or experience that in turn cost time and money to acquire.
-
Management workforce
Management and administrative positions of a company or organization , in charge of the directive and executive tasks of the productive circuit, are usually called management workforce . These are salaried but highly trained personnel, destined for trustworthy work and whose participation in the productive circuit is not direct, but of conduction.
-
Commercial labor
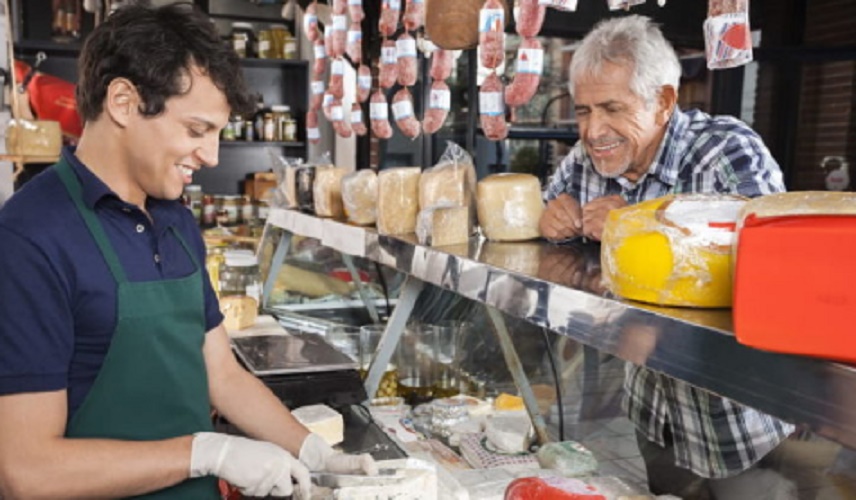

Commercial workers are known as all workers who are not directly linked to the product manufacturing circuit. On the contrary, they participate in their final stage of commercialization : distributors, sellers, merchants, etc.
They are more or less specialized forms of labor whose job is to deliver the product to its natural consumers and to finalize the economic transaction of its consumption.